This tree is beautiful, but sheds like crazy…
 |
| The canopy of the mighty oak |
Reminder of last week’s Challenge:
This is what the yard looks like up close:
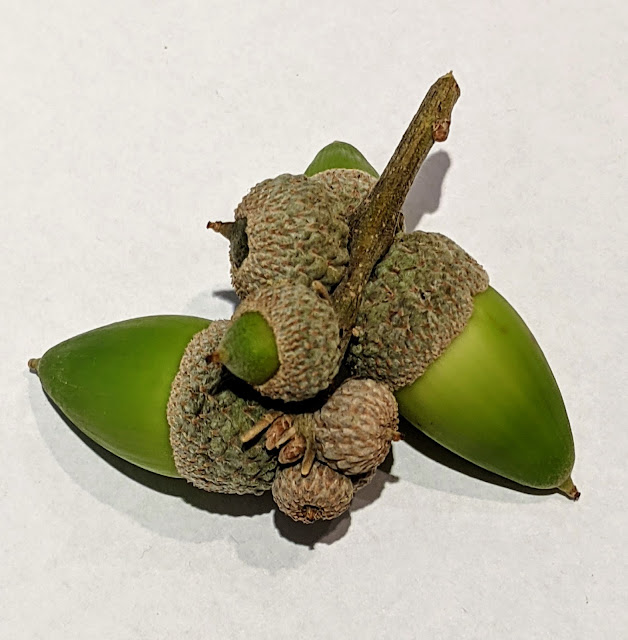
You can see a few leaves, an acorn, the cap of an acorn, and lots of those small brown knurled balls, each about 6mm (about 1/4 inch). I don’t know what they are, so I’ll call them nubbins until I figure out what they actually are. They’re everywhere. But what are they?
Here you see a typical branch end:
And a bit of a closeup so you can see the objects of interest…
The nubbins attach to the stem just above the acorn. Here you can see two of them, but often there will be 1, 2, 3 or 4 nubs. (Never more than that.)
And here’s a photo with everything taken apart:
And the Challenge?
1. What are those nubbin things? Is there a name for them?
2. What do they do for the tree? Why would a single tree generate so many of them? (I estimated, using Fermi estimation) that this tree produces around 100,000 of these per year. So over the past 10 years, that’s a cool 1 million nubbins (or whatever they are). What’s the point from the tree’s perspective?
To begin my Challenge SRS, I searched for [ black oak ] just to get some background information about the tree. (I wanted to start broad and narrow down.)
Much to my surprise, I quickly realized that this tree isn’t a black oak (Quercus velutina) at all! A black oak tree has very different leaves, and the acorn is also very different–it’s a big shaggy and the cap covers about half the nut. Compare this to the images of my tree up above! Nothing looked right. I had to question the tree’s identity!
I’m surprised by this, but perhaps I just misunderstood—maybe this is a California black oak (Quercus kelloggii). But no, the Q. kelloggii leaf looks like this (below: Leaves alternate, simple, 8-15 cm long, sharply cut into 7-11 lobes, toothed, each tooth ending in a bristle):
My oak tree doesn’t have sharp tips at the end (the lobes are squared-off and rounded), and the acorn of a kelloggi also has a cap that covers half the acorn. It’s not that either!
At this point I have to question what I know and embark on a new tree identification task.
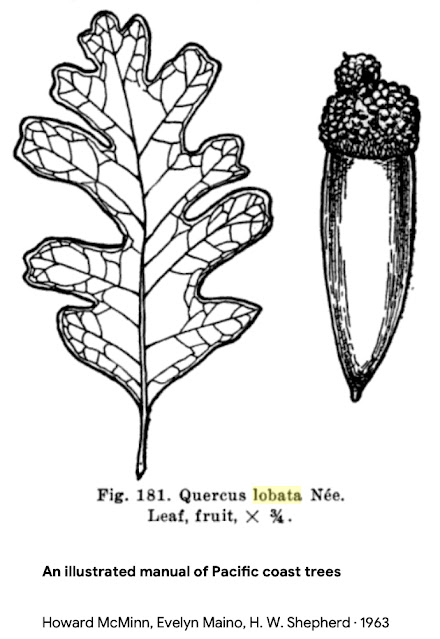
You’re SearchResearchers, so I won’t tell you all the ins-and-outs of my search (lots of searches for [ oaks in California ] and looking at oak tree identification keys (see SRS about keys), but I finally figured out that the oak tree in my backyard is a Valley oak (Quercus lobata – or see the definitive reference at the Jepson Herbarium). The leaves and acorns all look just the way they do in the first photo above.
Now that I’ve corrected my misunderstanding of what species of oak is hurting my feet, I can go back to trying to figure out what the nubs are.
I search for [ Quercus lobata acorn ] and start looking at pictures.
Interesting.
Oddly, almost every diagram / drawing / painting of a Valley oak acorn does NOT include the nubs. That seems strange, but it’s true. The illustrations all look a bit like this illustration. The leaves are right, the acorns are right, but there aren’t any nubbins.
 |
| P/C Rebecca Chamlee, Pie in the Sky Press |
This is a lovely image: Very neat, very clean, beautiful… and without nubbins. This is true of nearly all of the lobata illustrations you’ll find–they just don’t have the nubbins. What gives?
What’s really odd is that every picture of a real Valley oak acorn has a nubbin in image attached just above the acorn. (See my pic above with the red arrows. EVERY branch that has an acorn also has those nubbins attached.)
This is a great curiosity provoker: these things are everywhere, but nobody seems to talk about it!
After looking at many images of [ valley oak acorns ] I finally found an illustration with the nubbins:
See it at the top of the acorn? The sketch makes it look like the nubbin is very much like the cap of the acorn. Alas, there’s no note saying what that this is. But given its appearance: Is it possible that these are just immature acorns?
I take a stab at another search. My query is [ valley oak immature acorns ] guess what I found? Lots of images of small acorns growing at the tips of branches, looking exactly like slightly greener versions of my “nubbins.”
This prompted me to go out and look for a few more samples. Are the nubbins simply smaller acorns? Here’s a nice photo I took showing fully developed acorns, some very young acorns barely peeping out of the cup, and some “nubbins” that haven’t developed yet.
And, in a moment of inspiration, I took a few of the nubbins and did a cross-section of them. Take a look:
If you zoom in (just click on the pic above), you can see that in the center of each “nubbin” is a perfectly shaped tiny acorn nut.
I think we’ve solved our Challenge. The “nubbins” are simply immature acorns that are knocked off in a breeze or when a larger acorn detaches. The knurled appearance is simply the cap (technically, a cupule) of the acorn
Some SRS Regulars suggested that these might be galls. A gall is a trees response to a wasp laying an egg. Each species of oak has its own particular set of galls, many of which are very different from each other. Galls are so specific to a species that they’re one of the ways to determine oak species!
This is a photo of some valley oak galls–in the middle of each golf ball sized gall is a wasp larvae (or egg, depending on when you look at it). These conspicuous brown balls, do not much resemble an acorn. Also known as oak-apples, that result from a wasp depositing an egg, along with some plant hormone, to stimulate the growth of a protective home for the larva. Among the leaf litter at the base of the tree, one may find jumping galls about a millimeter in diameter that use the same strategy as the Mexican jumping bean, namely to reach shelter from the sun; when they land in a shady spot they cease jumping. These tiny galls also don’t look anything like an acorn.. or a nubbin.
SearchResearch Lessons
Sometimes the answer is obvious, once we learn how to see.
Search on! (Botanically!)